Effective Management of Stored Grain Pest
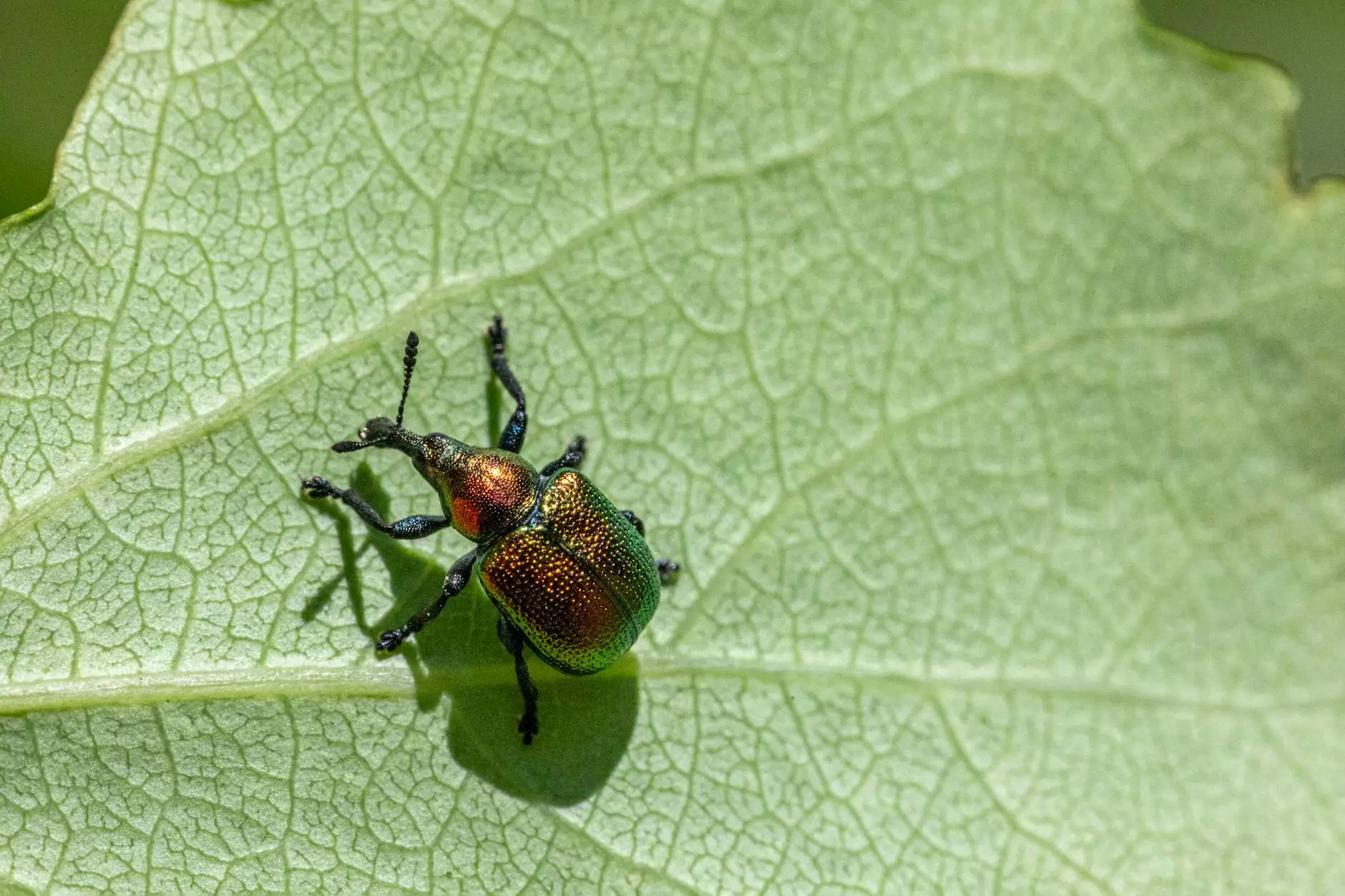

The management of stored grain pest is a critical aspect of agricultural success. Stored grain pests can severely impact the quality and quantity of grains stored, leading to significant economic losses. This article delves into effective strategies for controlling these pests, ensuring that farmers and grain processors can safeguard their precious harvest. By understanding the dynamics of stored grain pests, we can implement robust management practices that keep our grain safe from infestations.
Understanding Stored Grain Pests
Stored grain pests are a diverse group of insects and organisms that thrive in grain storage environments. They include weevils, moths, and beetles, which can cause extensive damage to grain stocks. Understanding these pests is the first step in effectively managing them.
Common Types of Stored Grain Pests
- Rice Weevil: Small, brownish-black insects that bore into grains.
- Granary Weevil: Similar to the rice weevil but primarily targets whole grains.
- Indian Meal Moth: A common pest that infests stored grain and other food products.
- Saw-Toothed Grain Beetle: A flat, brown beetle that can infest various grains and cereals.
- Darkling Beetle: Feeds on grain and is often found in storage facilities.
The Importance of Pest Management in Grain Storage
Implementing a comprehensive pest management plan is crucial for maintaining grain quality. Failure to address infestations can lead to:
- Reduced Grain Quality: Infestations can result in the deterioration of grain quality.
- Increased Economic Losses: Damaged grain often results in higher costs and reduced marketability.
- Health Risks: Some pests can contaminate grain with pathogens, posing health risks to consumers.
- Storage Challenges: Pest infestations complicate storage logistics and increase labor costs.
Strategies for Effective Management of Stored Grain Pests
A robust management of stored grain pest strategy involves multiple approaches. Let's examine these strategies in detail.
1. Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are the first line of defense against stored grain pests.
- Clean Storage Facilities: Regular cleaning helps eliminate food sources for pests.
- Proper Grain Handling: Ensure that grains are handled gently to prevent damage, which can attract pests.
- Temperature and Moisture Control: Maintaining optimal storage conditions can deter pest development.
- Regular Inspection: Frequent checks can catch infestations early, making control easier.
2. Monitoring and Identification
Effective pest management begins with accurate monitoring and identification of pest types. Using traps and visual inspections, farmers can assess the presence and types of pests in their grain stores.
Identification techniques include:
- Sticky Traps: Used to capture insects for identification.
- Pheromone Traps: Attract specific pests for monitoring.
- Visual Inspections: Regular checks for signs of infestation, such as larvae and frass (insect droppings).
3. Control Methods
Once pests are identified, the next step is applying control methods:
Biological Control
This involves using natural predators or competitors to control pest populations. For example, introducing certain parasitic wasps can help keep weevil populations in check.
Chemical Control
In certain cases, the application of insecticides may be necessary. It’s essential to select the right products and follow application guidelines to avoid harming non-target species or the environment.
Physical Control
This includes methods such as:
- Temperature Control: Freezing grain for several days can eliminate pests.
- Heat Treatment: Exposing grain to temperatures above 120°F (49°C) can kill insects.
- Vacuuming: Regular vacuuming of storage areas can help remove pests.
4. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive strategy that combines multiple methods for enhanced effectiveness and sustainability. IPM includes:
- Using a Combination of Controls: Integrating chemical, physical, and biological controls to create a more holistic approach.
- Cultural Practices: Adjusting farming practices to reduce pest habitat and food sources.
- Education and Training: Keeping farm staff informed on pest management practices and new technologies.
Benefits of Effective Pest Management
Implementing effective management strategies for stored grain pests can lead to numerous benefits:
- Preservation of Grain Quality: Maintaining the quality ensures market competitiveness.
- Increased Profitability: Reduced losses enhance overall profitability.
- Improved Safety: Protecting grains from contamination contributes to consumer safety.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing the need for chemical pesticides lowers environmental impact.
Conclusion
In summary, the management of stored grain pest is essential for any successful agricultural operation. By understanding the types of pests that threaten stored grains and employing a combination of preventive measures, monitoring strategies, and control methods, farmers can effectively manage these challenges. Emphasizing an integrated approach not only safeguards their harvests but also contributes to the sustainability of their farming practices.
For more insights and solutions on pest management, equipment repairs, and advancements in farming technology, visit tsgcinc.com.
Final Thoughts
As agriculture continues to evolve, so too must our strategies for pest management. Continuous education, innovation, and adaptation will be key in overcoming the challenges posed by stored grain pests. Let us work together towards a pest-free future and ensure the success of our farming endeavors.